links between metabolic health and lactation
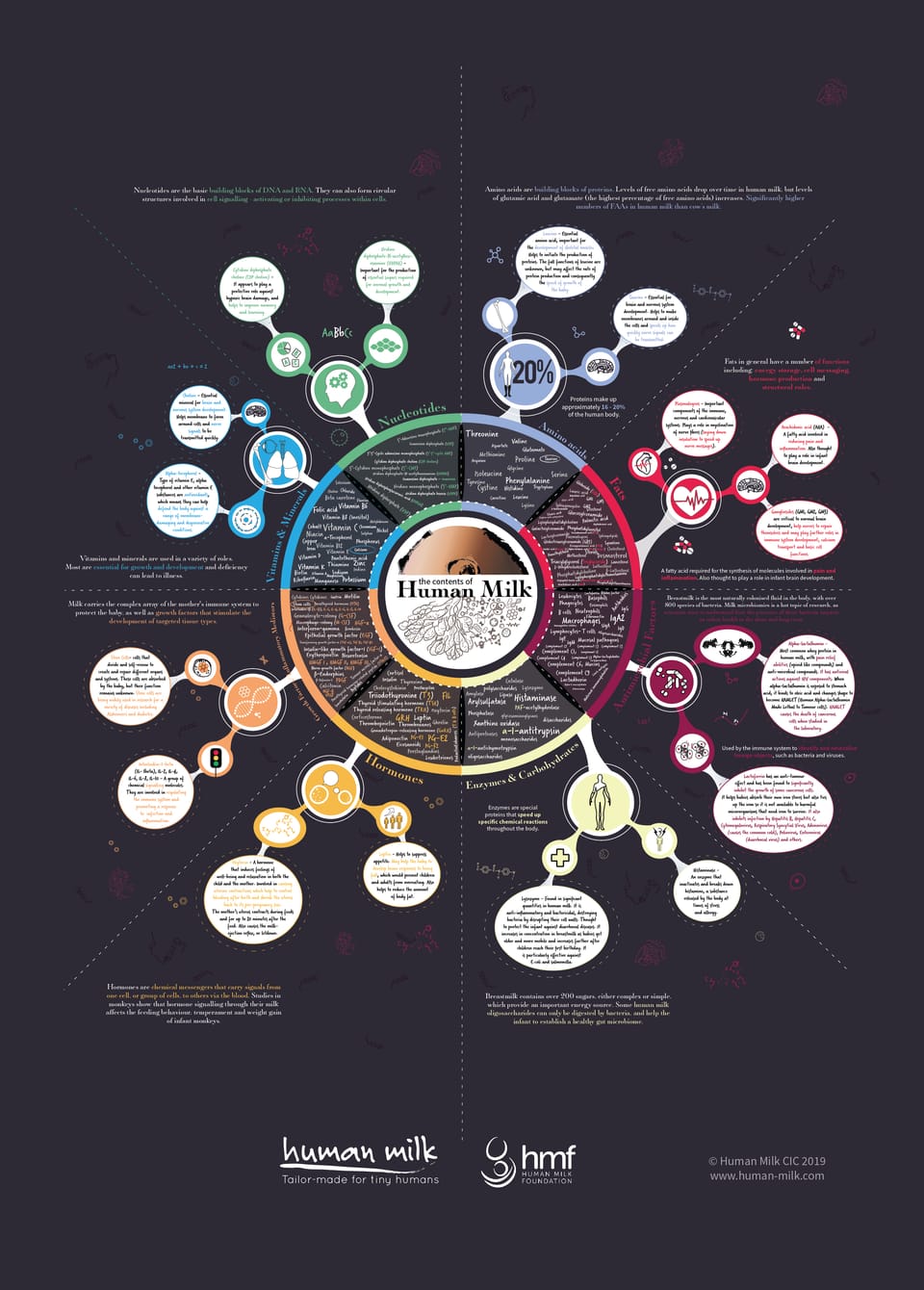
Precision or personalized medicine is being proclaimed as the wave of the future for healthcare. While us mere humans are at the tip of the proverbial iceberg when it comes to precision medicine, Mother Nature is light years ahead of us and the evidence is found in human breast milk. Recent research by Dr. Paula Meier out of Rush Medical Center shows increasing evidence that the milk of lactating parents truly is personalized medicine for very low birth weight infants (Meier, 2022). Very low birth weight infants (VLBW) were randomized to receive various proportions of mother’s own milk (MOM) and pasteurized donor human milk (PDHM) along with either human or bovine derived fortifier. Comparisons were made regarding gut microbial colonization, gut inflammation and oxidative stress. The researchers found that the type of human milk (parent versus donor) was more important than the type of fortifier in shaping gut microbiota and decreasing gut inflammation. Guess which milk seized the day? If you are thinking MOM…. you’re correct!
Other researchers across the globe concur that human milk is best for tiny humans in that it is dynamic and shows “high inter- and intra-individual variability” (Samuel, et al., 2020). Evidence exists for many of the infant related factors known to affect the nutritive and non-nutritive components of human milk. Think birth weight, gestational age, infant age/stage of lactation and so on. What we don’t know much about yet through research is the effect of maternal factors on breast milk. However, a 2022 systemic review of 12 studies points to the idea that gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is associated with not only low milk supply but also with milk composition when compared to non-GDM lactating parents in preliminary studies (Suwaydi, et al., 2022). The altered milk composition is suspected to negatively affect infant weight gain as well as lean body mass/adiposity ratios. But, as always, more research needs to be done!
References
Meier, P. (2022). More evidence: mothers’ own milk is personalized medicine for very low birthweight infants. Cell Reports Medicine 3 (8), 100710. https://doi.org/10.1016/jxcem.2022.100710
Samuel, T.M., et al. (2020). Nutritional and non-nutritional composition of human milk is modulated by maternal, infant, and methodological factors. Frontiers in Nutrition 2020 (7), 576138. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2020.576133
Suwaydi, M.A,, et al.(2022). The impact of gestational diabetes mellitus on human milk metabolic hormones: a systemic review. Nutrients 2022 14 (17), 3620. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14173620